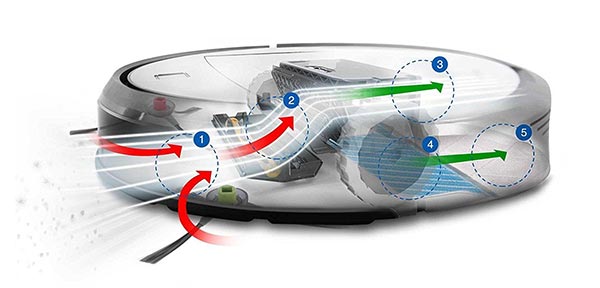
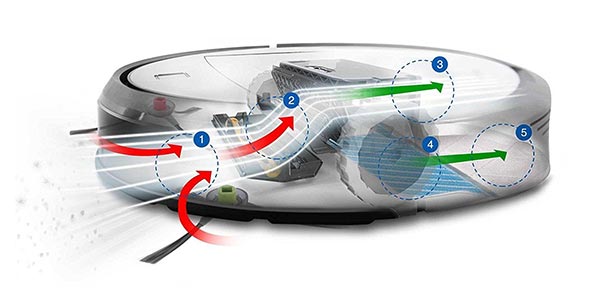
How Do Robot Vacuums Find Their Base?

Most robot vacuums have sensors that allow them to find their base. When the vacuum’s battery is running low, it will search for its base and dock itself so that it can recharge. The sensors help the vacuum avoid obstacles and furniture while it cleans.
Robot vacuums are amazing little machines that can keep your floors clean with very little effort on your part. But have you ever wondered how they find their way back to their base? It’s actually pretty simple.
Most robot vacuums use infrared sensors to detect when they are close to their base. The sensors emit a beam of infrared light and when the beam is interrupted, it means the vacuum is close to its target. The vacuum will then slow down and carefully make its way back to the base.
Some higher-end models may use GPS or other more sophisticated methods to find their way home, but the vast majority of robot vacuums rely on good old fashioned infrared sensors. So next time you see your robot vacuum zooming around, you’ll know how it knows where to go.
The Amazing Engineering behind the Cleaning Robots!
How Does Roomba Know Where Home Base Is?
Roomba’s home base is a small, circular docking station that it returns to automatically when its batteries are running low. The home base serves as both a charger and a cleaning storage unit for the Roomba.
How does Roomba know where home base is?
Each Roomba comes with a virtual wall unit that emits an invisible infrared beam. This beam tells the Roomba where the boundaries of a room are so that it doesn’t go wandering off into another room (or fall down the stairs!). The home base unit also emits an infrared beam, but this beam is different from the virtual wall beams.
When the Roomba’s batteries start to run low, it will begin to search for its home base. The homebase unit emits a stronger infrared signal than the virtual wall units, so the Roomba will be able to follow the signal back to its dock.
How Does Roomba Know Where the Dock Is?
When you first set up your Roomba, you will need to create a virtual wall or barrier that tells the device where your home’s boundaries are. Once it has this information, it can start cleaning and will automatically return to its dock when it is finished or when it needs to recharge.
How does Roomba know where the dock is?
Roombas use a combination of sensors and mapping technology to find their way around your home and locate their docking station. The sensors help the Roomba avoid obstacles and furniture, while the mapping technology allows it to create a mental picture of your floor plan and remember where the dock is located.
One of the most important things for a Roomba is to know where its dock is located.
After all, that’s where it goes to rest and recharge in between cleanings. But how does this little robot vacuum manage to find its way back time after time? Let’s take a closer look at how Roombas know where the dock is.
There are actually two ways that Roombas use to find their docks: sensors and mapping. Both methods play an important role in helping these devices keep track of their location so they can make their way back when needed.
How Does Shark Robot Find Dock?
Shark robot comes with a special dock that it can find and return to automatically. The dock has a GPS locator and an infrared beacon. Once the Shark robot is placed in the water, it uses these two signals to determine its location and then plot a course back to the dock.
Where Should I Put My Robot Vacuum Base?
Assuming you are referring to a Roomba base: The best place for your Roomba base is on a hard, flat surface in an open area. If possible, avoid putting the base near walls or furniture, as this can block the signal and prevent the Roomba from docking properly.
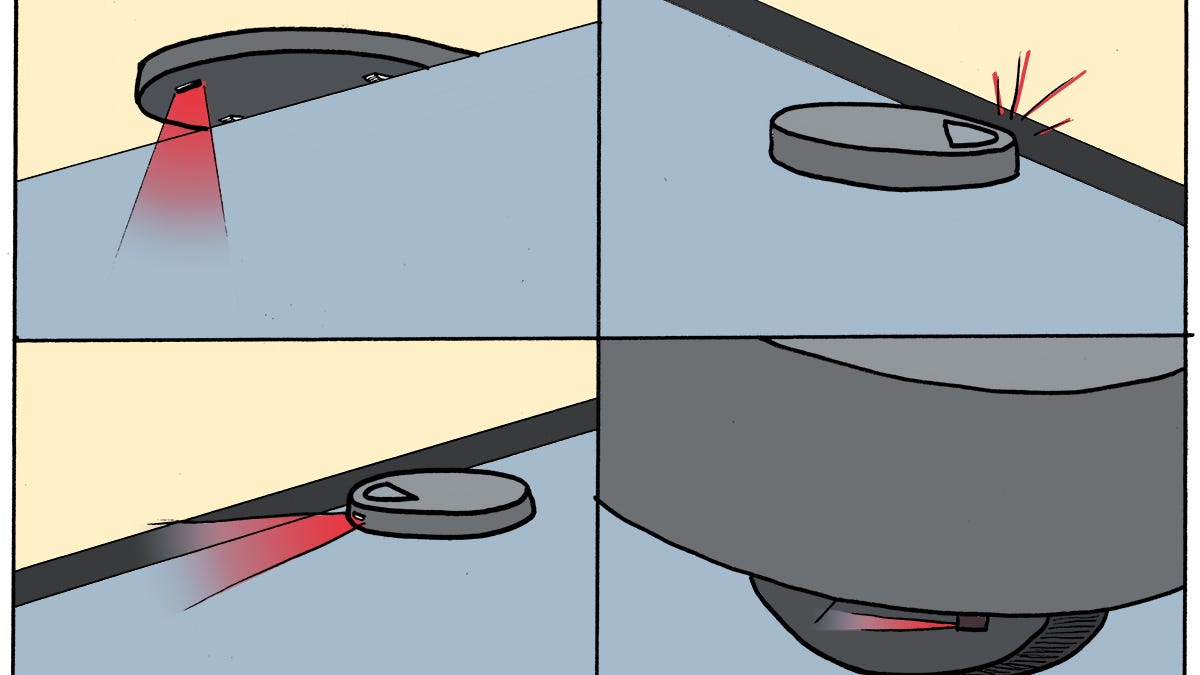
Credit: www.cnet.com
How Does Robot Vacuum Mapping Work
Are you curious about how those nifty little robot vacuums create a map of your home? Well, wonder no more! In this blog post, we’ll explore how robot vacuums use mapping technology to clean your home more efficiently.
Robot vacuums are equipped with sensors that help them navigate their surroundings. As the vacuum cleans, it uses these sensors to create a map of the area. This map allows the vacuum to plan its cleaning route and avoid obstacles.
Some robot vacuums use LiDAR (light detection and ranging) technology to create their maps. This involves shining a laser onto surfaces and measuring the time it takes for the light to bounce back. By doing this, the vacuum can create a 3D map of its surroundings.
Other robot vacuums use visual SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) algorithms to create 2D maps. This involves taking pictures of the area as it cleans and using these images to build a map. The advantage of this method is that it doesn’t require any special hardware like LiDAR; however, it is not as accurate as LiDAR mapping.
Once the robot vacuum has created a map of your home, it stores this information in its memory so that it can access it later. This way, if you move furniture around or make other changes to your home’s layout, the vacuum will be able to adjust its cleaning route accordingly. So there you have it.
That’s how robot vacuums use mapping technology to clean your home more effectively. Do you have any questions about how this process works? Feel free to ask in the comments below!
Conclusion
Robot vacuums are becoming increasingly popular, but how do they find their way back to their base? It turns out that there are a few different ways that manufacturers have developed to help robot vacuums find their way home.
Some robot vacuums use an infrared remote control.
The user sets up the base station in the desired location and presses a button on the remote to tell the vacuum where to return. Other models use GPS tracking, which is more accurate but requires an additional investment.
The most common method, however, is simply using sensors to detect when the vacuum has reached the edge of a room or piece of furniture.
The vacuum will then turn and continue cleaning until it has covered the entire area. Once it has finished, it will make its way back to the base station by following the path it took when it first started cleaning.